什么是可重入?什么是可重入锁?它用来解决什么问题?
ReentrantLock 的核心是 AQS,那么它怎么来实现的,继承吗?说说其类内部结构关系
ReentrantLock 是如何实现公平锁的?
ReentrantLock 是如何实现非公平锁的?
ReentrantLock 默认实现的是公平还是非公平锁?
使用 ReentrantLock 实现公平和非公平锁的示例?
ReentrantLock 和Synchronized 的对比?
ReentrantLock 的特点 显式锁定与解锁 ReentrantLock 需要显式地调用 lock() 方法进行锁定,而在不再需要锁时,需要调用 unlock() 方法解锁。这与 synchronized 关键字的隐式锁定机制不同,后者由JVM自动管理锁定和解锁的过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ();lock.lock(); try { } finally { lock.unlock(); }
可重入性 ReentrantLock 是一个 可重入锁 ,这意味着如果一个线程已经持有了该锁,它可以多次获取锁而不会造成死锁。例如,如果某个线程调用了 lock() 多次,那么它必须调用相同次数的 unlock() 才能真正释放锁
公平锁与非公平锁 ReentrantLock 可以配置为 公平锁 或 非公平锁 。公平锁保证了线程获取锁的顺序是按照请求锁的顺序来进行的(即 FIFO 队列),而非公平锁则是默认的方式,可能会打破请求顺序,导致某些线程可能会「插队」
1 2 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock (true ); ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock (false );
尝试加锁 与 synchronized 不同,ReentrantLock 提供了 tryLock() 方法,允许线程在尝试获取锁时不阻塞。如果锁没有被其他线程持有,则 tryLock() 会立即返回 true,否则返回 false。这个特性可以用于避免长时间的等待
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (lock.tryLock()) { try { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } else { }
还有一个带超时时间的版本 tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit),它允许线程在指定的时间内等待锁
条件变量 ReentrantLock 提供了 newCondition() 方法来创建一个或多个 Condition 对象,用于线程间通信。Condition 类似于 synchronized 中的 wait() 和 notify()/notifyAll(),但其功能更为灵活,可以创建多个条件变量以精细控制线程的等待和唤醒
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ();Condition condition = lock.newCondition();lock.lock(); try { condition.await(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } lock.lock(); try { condition.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); }
中断响应 ReentrantLock 支持中断。线程在等待获取锁时可以被中断,这在 synchronized 中是不支持的。可以通过 lockInterruptibly() 方法来实现中断响应
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 try { lock.lockInterruptibly(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); }
ReentrantLock 的核心原理 ReentrantLock 的核心原理基于底层的 CAS(Compare-And-Swap)机制 和 AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)框架 ,这是它实现线程安全、重入性、锁竞争管理等特性的基础
锁的获取 ReentrantLock 的锁获取操作是通过 AQS 提供的 acquire() 方法来实现的。在锁的获取过程中,可能涉及到以下几种情况:
初次获取锁 :
如果锁未被任何线程占用(state == 0),线程通过 CAS 操作将 state 设置为 1,表示成功获取锁
锁的重入 :
如果锁已经被当前线程占用,线程可以再次调用 lock(),这时 state 的值会递增,记录锁的重入次数
当线程多次重入锁时,每调用一次 unlock(),state 值会递减一次,直到 state == 0 时锁才真正被释放
锁竞争 :
如果锁已经被其他线程持有,当前线程将会被挂起,进入 AQS 维护的 FIFO 队列,等待被唤醒
等待队列中的线程将按照先后顺序依次被唤醒,尝试获取锁
公平锁与非公平锁 公平锁 :在公平锁中,锁的获取顺序按照线程请求锁的顺序来进行,避免「插队」。公平锁通过检查等待队列是否有其他线程,如果有,当前线程必须进入队列等待。
非公平锁 :非公平锁允许线程「插队」,即当线程请求锁时,它会直接尝试用 CAS 获取锁,而不是检查等待队列中的线程。非公平锁可能会导致某些线程饥饿(长时间无法获取锁),但通常性能更好,因为减少了对队列的检查
锁的释放 锁的释放通过 AQS 的 release() 方法来实现:
当前线程调用 unlock() 时,会将 state 值减 1
如果 state 值变为 0,表示锁已完全释放,AQS 会将等待队列中的第一个线程唤醒,使其尝试获取锁
唤醒的线程再次尝试通过 CAS 更新 state,如果成功,则获取锁
条件变量 ReentrantLock 支持条件变量(Condition),这也是由 AQS 提供的。条件变量通过 await() 和 signal() 等方法实现线程间通信。
**await()**:当线程调用 condition.await(),它会释放当前锁并进入条件等待队列,同时阻塞线程
**signal()**:当其他线程调用 condition.signal(),会从条件等待队列中选择一个线程唤醒,使其重新尝试获取锁
中断响应 ReentrantLock 提供了对线程中断的支持,特别是在使用 lockInterruptibly() 时,当线程在获取锁的过程中被中断,AQS 会将其从等待队列中移除,并抛出 InterruptedException,让线程响应中断
ReentrantLock 简单示例 可重入性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ();public void methodA () { lock.lock(); try { System.out.println("methodA is executing..." ); methodB(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void methodB () { lock.lock(); try { System.out.println("methodB is executing..." ); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { ReentrantLockTest test = new ReentrantLockTest (); test.methodA(); }
Out:
1 2 methodA is executing... methodB is executing...
公平锁与非公平锁 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 private static class Worker implements Runnable { private final ReentrantLock lock; public Worker (ReentrantLock lock) { this .lock = lock; } @Override public void run () { lock.lock(); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Worker is running" ); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { if (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock (true ); ReentrantLock nonFairLock = new ReentrantLock (false ); List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { threads.add(new Thread (new Worker (fairLock), "T-" + i)); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { Thread currT = threads.get(i); if (i == 0 ) { currT.start(); } else { Thread preT = threads.get(i - 1 ); Thread.State preTState; while (true ) { preTState = preT.getState(); if (preTState == Thread.State.WAITING || preTState == Thread.State.TIMED_WAITING) { currT.start(); break ; } } } System.out.println("T-" + i + " start..." ); } }
Out(公平锁):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 T-0 start... T-0: Worker is running T-1 start... T-2 start... T-3 start... T-4 start... T-5 start... T-6 start... T-7 start... T-8 start... T-9 start... T-1: Worker is running T-2: Worker is running T-3: Worker is running T-4: Worker is running T-5: Worker is running T-6: Worker is running T-7: Worker is running T-8: Worker is running T-9: Worker is running
非公平锁的情景我运行了许多次,始终没能出现相应的打印….
条件变量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock ();private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();private final Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList <>();private final int capacity = 5 ;void produce (int value) throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.size() == capacity) { System.out.println("Queue is full, producer is waiting..." ); notFull.await(); } queue.offer(value); System.out.println("Producer >>> " + value); notEmpty.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } void consume () throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Queue is empty, consumer is waiting..." ); notEmpty.await(); } Integer value = queue.poll(); System.out.println("Consumer <<< " + value); notFull.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { ReentrantLockTest3 test3 = new ReentrantLockTest3 (); Thread producerThread = new Thread (() -> { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { try { test3.produce(i); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); Thread consumerThread = new Thread (() -> { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { try { test3.consume(); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(250 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); producerThread.start(); consumerThread.start(); }
在使用 Condition 时,必须先持有对应的锁,这个和 Object 类的 wait()、notify()、notifyAll() 方法类似,必须先持有某个对象的监视器锁,才能执行
ArrayBlockingQueue 采用了上面例子的方式实现了生产者-消费者,实际生产中可以直接使用 ArrayBlockQueue
Out:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Producer >>> 0 Consumer <<< 0 Producer >>> 1 Producer >>> 2 Consumer <<< 1 Producer >>> 3 Producer >>> 4 Consumer <<< 2 Producer >>> 5 Producer >>> 6 Producer >>> 7 Consumer <<< 3 Producer >>> 8 Queue is full, producer is waiting... Consumer <<< 4 Producer >>> 9 Consumer <<< 5 Consumer <<< 6 Consumer <<< 7 Consumer <<< 8 Consumer <<< 9
中断响应 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ();private void performTask () { try { lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " acquired lock" ); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5 ); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " interrupted" ); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReentrantLockTest4 test4 = new ReentrantLockTest4 (); Thread t1 = new Thread (test4::performTask); Thread t2 = new Thread (test4::performTask); t1.start(); t2.start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2 ); if (t1.getState() == Thread.State.WAITING) { t1.interrupt(); } else { t2.interrupt(); } }
Out:
1 2 Thread-0 acquired lock Thread-1 interrupted
ReentrantLock 源码解析 ReentrantLock 实现了 Lock 接口,虽然 ReentrantLock 继承了很多 AQS 的方法,但是它自身并没有直接继承 AQS,而是通过它的内部类继承 AQS 的
关键属性 ReentrantLock 只有两个属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class ReentrantLock implements Lock , java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L ; private final Sync sync; }
sync 是 ReentrantLock 中的关键属性
ReentrantLock 的大部分操作其本质是对 sync 属性的操作
而 sync 的对象是 ReentrantLock 的一个内部类
关键内部类 抽象内部类 Sync
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L ; abstract void lock () ; final boolean nonfairTryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0 ) { if (compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(nextc); return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); boolean free = false ; if (c == 0 ) { free = true ; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); } setState(c); return free; } protected final boolean isHeldExclusively () { return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread(); } final ConditionObject newCondition () { return new ConditionObject (); } final Thread getOwner () { return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread(); } final int getHoldCount () { return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0 ; } final boolean isLocked () { return getState() != 0 ; } private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); setState(0 ); } }
公平锁内部类 FairSync
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static final class FairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L ; final void lock () { acquire(1 ); } protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0 ) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(nextc); return true ; } return false ; } }
非公平内部类 NonfairSync :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L ; final void lock () { if (compareAndSetState(0 , 1 )) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1 ); } protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); } }
关键方法 构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ReentrantLock () { sync = new NonfairSync (); } public ReentrantLock (boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync () : new NonfairSync (); }
获取锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 public void lock () { sync.lock(); } public boolean tryLock () { return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1 ); } public boolean tryLock (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1 , unit.toNanos(timeout)); } public final boolean tryAcquireNanos (int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); return tryAcquire(arg) || doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout); } private boolean doAcquireNanos (int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException { if (nanosTimeout <= 0L ) return false ; final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout; final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE); boolean failed = true ; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return true ; } nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime(); if (nanosTimeout <= 0L ) return false ; if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold) LockSupport.parkNanos(this , nanosTimeout); if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
条件变量相关
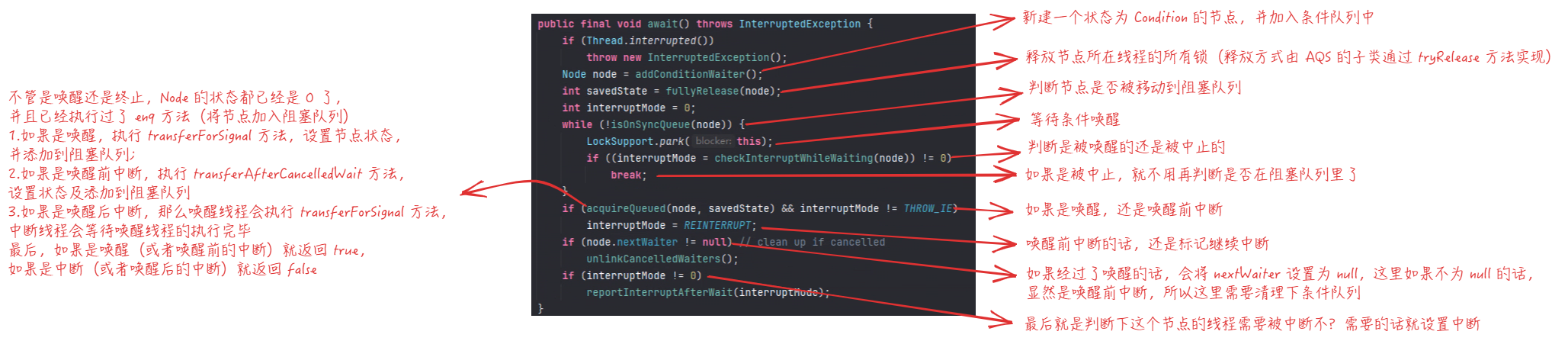
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 final ConditionObject newCondition () { return new ConditionObject (); } public class ConditionObject implements Condition , java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L ; private transient Node firstWaiter; private transient Node lastWaiter; public ConditionObject () {} public final void await () throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this ); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); } private Node addConditionWaiter () { Node t = lastWaiter; if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { unlinkCancelledWaiters(); t = lastWaiter; } Node node = new Node (Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION); if (t == null ) firstWaiter = node; else t.nextWaiter = node; lastWaiter = node; return node; } private void unlinkCancelledWaiters () { Node t = firstWaiter; Node trail = null ; while (t != null ) { Node next = t.nextWaiter; if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { t.nextWaiter = null ; if (trail == null ) firstWaiter = next; else trail.nextWaiter = next; if (next == null ) lastWaiter = trail; } else trail = t; t = next; } } private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1 ; private static final int THROW_IE = -1 ; private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting (Node node) { return Thread.interrupted() ? (transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) : 0 ; } public final void signal () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null ) doSignal(first); } private void doSignal (Node first) { do { if ((firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null ) lastWaiter = null ; first.nextWaiter = null ; } while (!transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null ); } public final void signalAll () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null ) doSignalAll(first); } private void doSignalAll (Node first) { lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null ; do { Node next = first.nextWaiter; first.nextWaiter = null ; transferForSignal(first); first = next; } while (first != null ); } public final void awaitUninterruptibly () { Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); boolean interrupted = false ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this ); if (Thread.interrupted()) interrupted = true ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted) selfInterrupt(); } private void reportInterruptAfterWait (int interruptMode) throws InterruptedException { if (interruptMode == THROW_IE) throw new InterruptedException (); else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT) selfInterrupt(); } public final long awaitNanos (long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout; int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { if (nanosTimeout <= 0L ) { transferAfterCancelledWait(node); break ; } if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold) LockSupport.parkNanos(this , nanosTimeout); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime(); } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); return deadline - System.nanoTime(); } public final boolean awaitUntil (Date deadline) throws InterruptedException { long abstime = deadline.getTime(); if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); boolean timedout = false ; int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { if (System.currentTimeMillis() > abstime) { timedout = transferAfterCancelledWait(node); break ; } LockSupport.parkUntil(this , abstime); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); return !timedout; } public final boolean await (long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { long nanosTimeout = unit.toNanos(time); if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout; boolean timedout = false ; int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { if (nanosTimeout <= 0L ) { timedout = transferAfterCancelledWait(node); break ; } if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold) LockSupport.parkNanos(this , nanosTimeout); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime(); } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); return !timedout; } final boolean isOwnedBy (AbstractQueuedSynchronizer sync) { return sync == AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this ; } protected final boolean hasWaiters () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null ; w = w.nextWaiter) { if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) return true ; } return false ; } protected final int getWaitQueueLength () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); int n = 0 ; for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null ; w = w.nextWaiter) { if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) ++n; } return n; } protected final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList <Thread>(); for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null ; w = w.nextWaiter) { if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) { Thread t = w.thread; if (t != null ) list.add(t); } } return list; } }
AQS 中提供相关条件控制的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 final int fullyRelease (Node node) { boolean failed = true ; try { int savedState = getState(); if (release(savedState)) { failed = false ; return savedState; } else { throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); } } finally { if (failed) node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; } } public final boolean release (int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0 ) unparkSuccessor(h); return true ; } return false ; } final boolean isOnSyncQueue (Node node) { if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null ) return false ; if (node.next != null ) return true ; return findNodeFromTail(node); } private boolean findNodeFromTail (Node node) { Node t = tail; for (;;) { if (t == node) return true ; if (t == null ) return false ; t = t.prev; } } final boolean transferForSignal (Node node) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0 )) return false ; Node p = enq(node); int ws = p.waitStatus; if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL)) LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); return true ; } final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait (Node node) { if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0 )) { enq(node); return true ; } while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) Thread.yield (); return false ; }
核心流程 ReentrantLock 加锁与释放锁的过程就是上篇 AQS 中的过程
这里主要分析 ReentrantLock 的条件变量处理过程
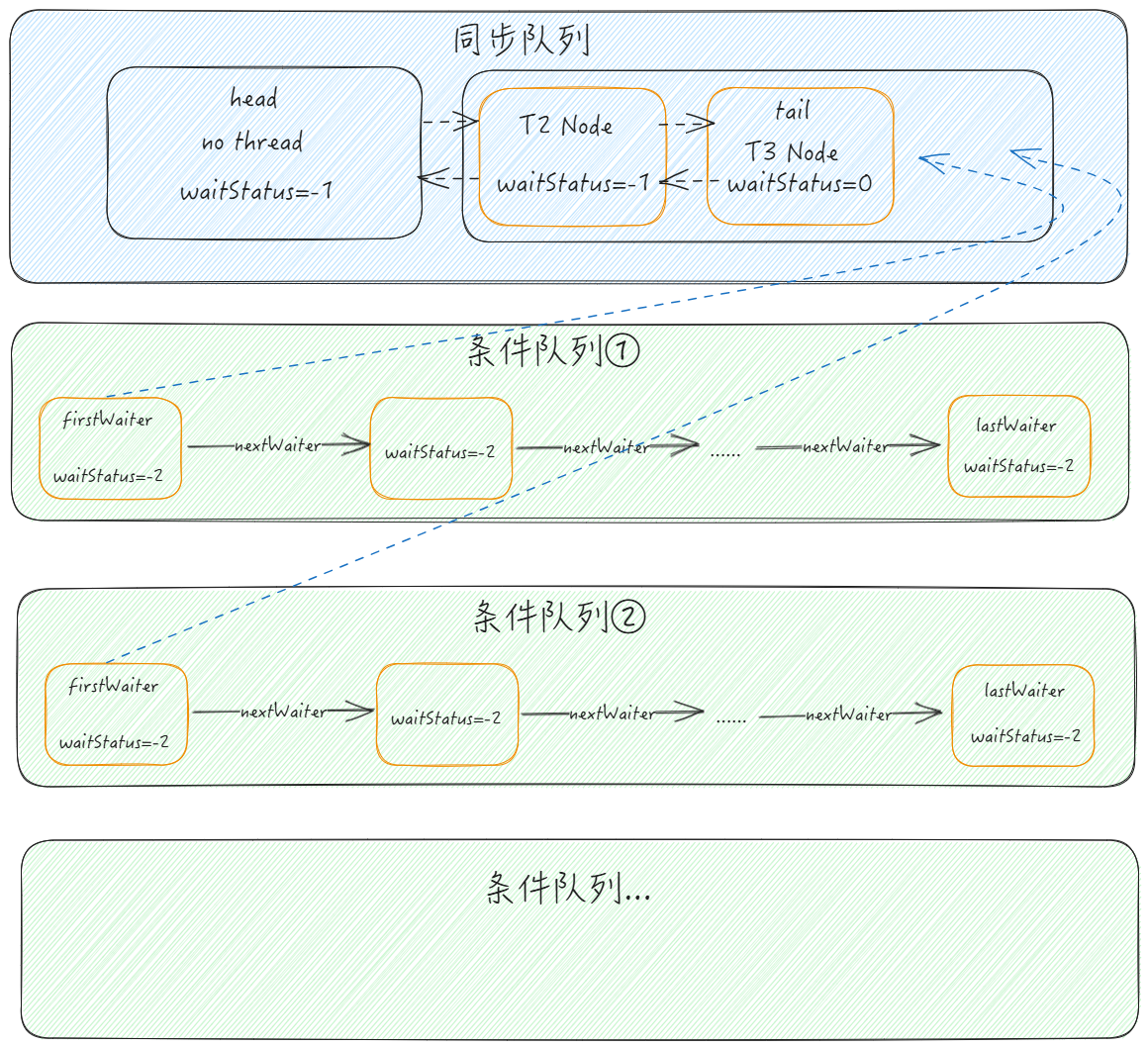
其实 await 中已经涵盖了 signal 了,signal 的关键在于 transferForSignal 方法,而 transferForSignal 的关键又在于其对 waitStatus 的判断以及线程的唤醒
等待与唤醒过程中同步队列与条件队列的变化
虚假唤醒 不管是 ReentrantLock 中的 await,还是 Synchronized 中的 wait,它们都会出现虚假唤醒的情况。虚假唤醒是并发编程中的一个普遍现象,不仅存在于 Java 中,在其他编程语言和并发系统中也可能发生。这是因为虚假唤醒通常源于底层系统的实现细节,而不是语言特性。
通常,需要使用 while 来检查条件是否满足,而不是 if
上面生产者-消费者的例子中,如果将 while 改为 if,可以观察到虚假唤醒的情况发生