从 二叉树 到 二叉搜索树(binary search tree) 到 平衡二叉树(AVL tree) 再到 红黑树( Red-Black tree) 最后实现 TreeMap 和 TreeSet
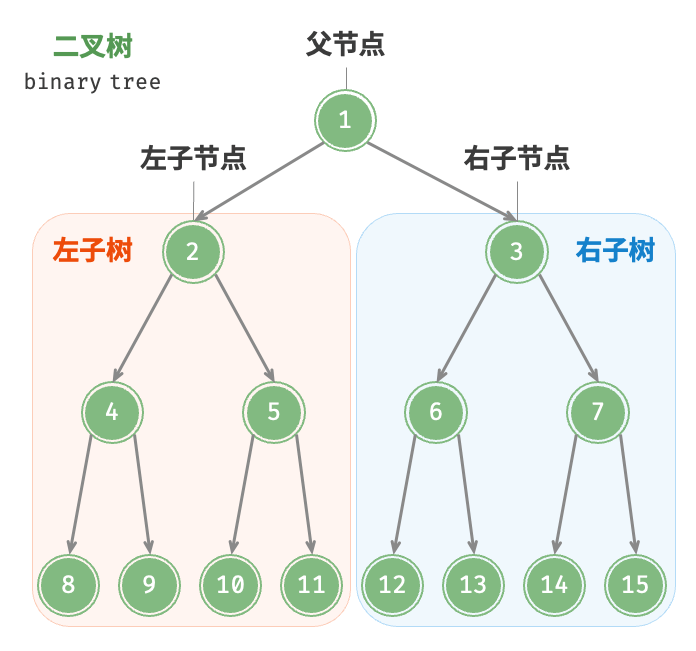
二叉树 与链表类似,二叉树的基本单元是节点,每个节点包含值、左子节点引用和右子节点引用,代表「父」与「子」之间的派生关系,体现了「一分为二」的分治逻辑
根节点 :位于二叉树顶层,没有父节点(节点 1)叶节点 :没有子节点的节点,其两个指针均指向 None(节点 8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15)边 :连接两个节点的线段,即节点引用(指针)节点所在的层 :从顶至底递增,根节点所在层为 1 (节点 4 在第 3 层)节点所在的度 :节点的子节点的数量。在二叉树中,度的取值范围是 0、1、2(2)二叉树的高度 :从根节点到最远叶节点所经过的边的数量(高度为 3)节点的深度 :从根节点到该节点所经过的边的数量(节点 4 的深度为 2)节点的高度 :从距离该节点最远的叶节点到该节点所经过的边的数量(节点 4 的高度为 1)
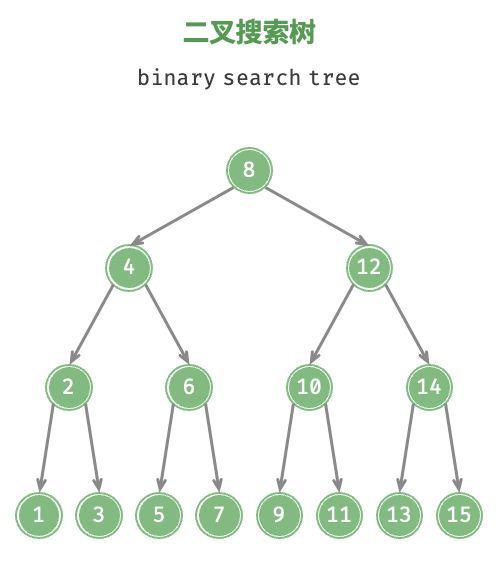
二叉搜索树 当一个二叉树满足以下条件,便可称为二叉搜索树:
左子树中所有节点的值 < 根节点的值 < 右子树中所有节点的值
左右子树也满足条件 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 public class BinarySearchTree <T extends Comparable <T>> { private Node<T> root; public BinarySearchTree () { root = null ; } public void put (T data) { root = insert(root, data); } private Node<T> insert (Node<T> root, T data) { if (root == null ) { return new Node <>(data); } if (data.compareTo(root.data) < 0 ) { root.left = insert(root.left, data); } else if (data.compareTo(root.data) > 0 ) { root.right = insert(root.right, data); } else { System.out.println("已存在" ); } return root; } public void delete (T data) { root = delete(root, data); } private Node<T> delete (Node<T> root, T data) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } if (data.compareTo(root.data) < 0 ) { root.left = delete(root.left, data); } else if (data.compareTo(root.data) > 0 ) { root.right = delete(root.right, data); } else { if (root.left == null ) { return root.right; } else if (root.right == null ) { return root.left; } else { Node<T> temp = findMin(root.right); root.data = temp.data; root.right = delete(root.right, temp.data); } } return root; } private Node<T> findMin (Node<T> root) { while (root.left != null ) { root = root.left; } return root; } static class Node <T> { T data; Node<T> left; Node<T> right; public Node (T data) { this .data = data; } public Node (T data, Node<T> left, Node<T> right) { this .data = data; this .left = left; this .right = right; } } }
二叉搜索树对插入的顺序有要求
二叉搜索树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度都是 O(logn)
最为复杂的是删除操作,删除时为了保证 左子树中所有节点的值 < 根节点的值 < 右子树中所有节点的值,删除时会取删除节点的 右子树中最小叶节点,将删除节点的值替换为叶节点的值,并删除右子树中该叶节点(详见 delete 方法)
DFS 与 BFS 关于二叉搜索树的遍历,存在两种遍历方式
深度优先搜索
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private void printDFS (Node<T> root) { List<List<Node<T>>> result = new ArrayList <>(); dfs(root, 0 , result); for (List<Node<T>> list : result) { for (Node<T> node : list) { System.out.print(node == null ? "N " : node.data + " " ); } System.out.println(); } } private void dfs (Node<T> root, int level, List<List<Node<T>>> result) { if (level == result.size()) { if (root != null ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(List.of(root))); } else { return ; } } else { if (root != null ) { result.get(level).add(root); } else { result.get(level).add(null ); return ; } } dfs(root.left, level + 1 , result); dfs(root.right, level + 1 , result); }
广度优先搜索
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private void printBFS (Node<T> root) { LinkedList<Node<T>> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int levelSize = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < levelSize; i++) { Node<T> node = queue.removeFirst(); if (node != null ) { System.out.print(node.data + " " ); } else { System.out.print("N " ); continue ; } queue.add(node.left); queue.add(node.right); } System.out.println(); } }
平衡二叉树 由于二叉搜索树的结构与插入及删除有关,这样其结构就会出现不可控,可能会退化为链表,这样所有操作的时间复杂度将变为 O(n)
因此,一个能在插入和删除时自动平衡树结构的平衡二叉树应运而生
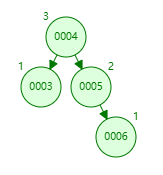
节点高度 平衡二叉树在二叉树的基础上增加了一个属性——高度
高度用来表示该节点处于平衡二叉树的层级,叶子节点的高度为 1,每距离叶子节点一个单位则高度 +1,如果左右子树的高度不一致,则取最高子树的高度
上图中,两个叶子节点 0003 和 0006 层高为 1,0005 层高为 2,根节点 0004 取较高的右子树高度 3
平衡因子 平衡因子是决定平衡二叉树是否启动自平衡的关键,通常 -1 ≤ 平衡因子 ≤ 1 时不需要调整,否则进行自平衡
某节点的平衡因子 = 该节点左子树高度 - 该节点右子树高度
如上图,
0004 节点的平衡因子 = 1 - 2 = -1
0005 节点的平衡因子 = 0 - 1 = -1
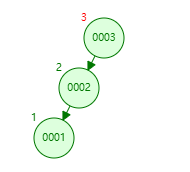
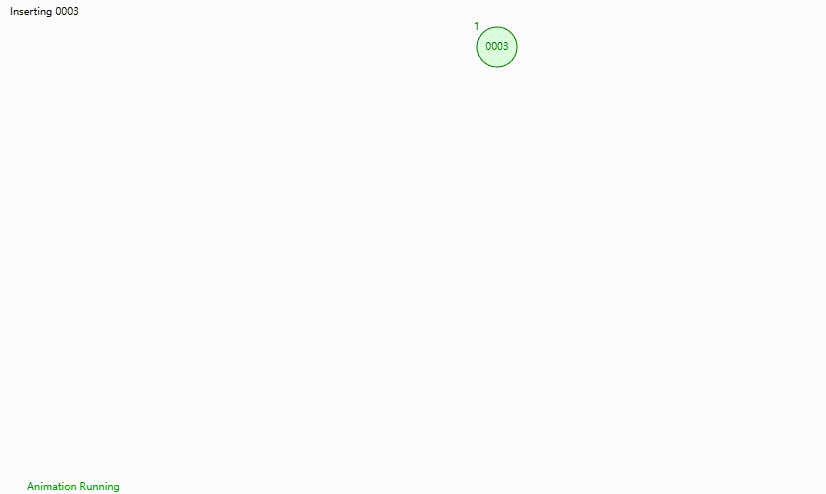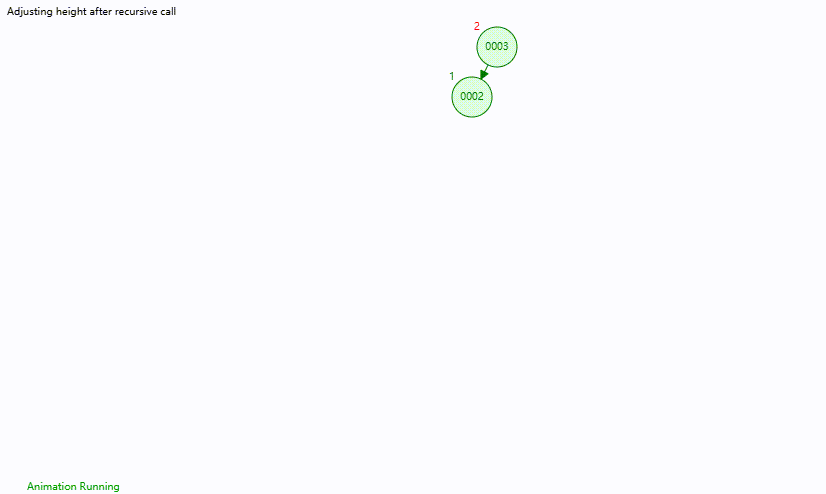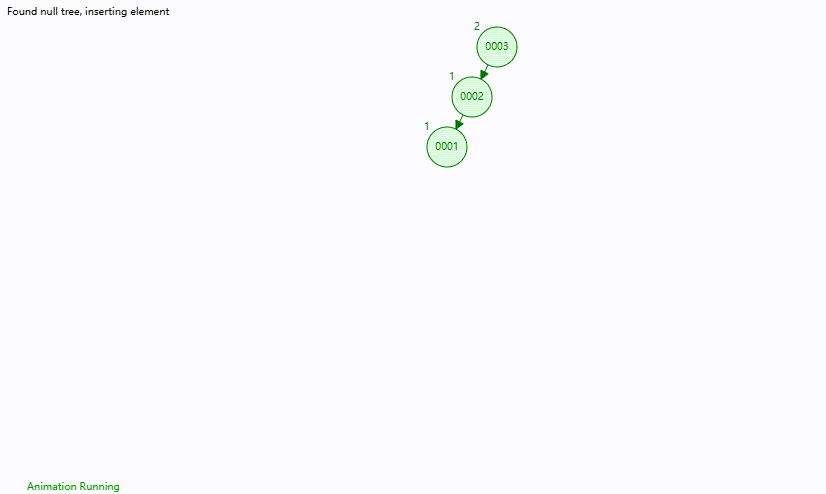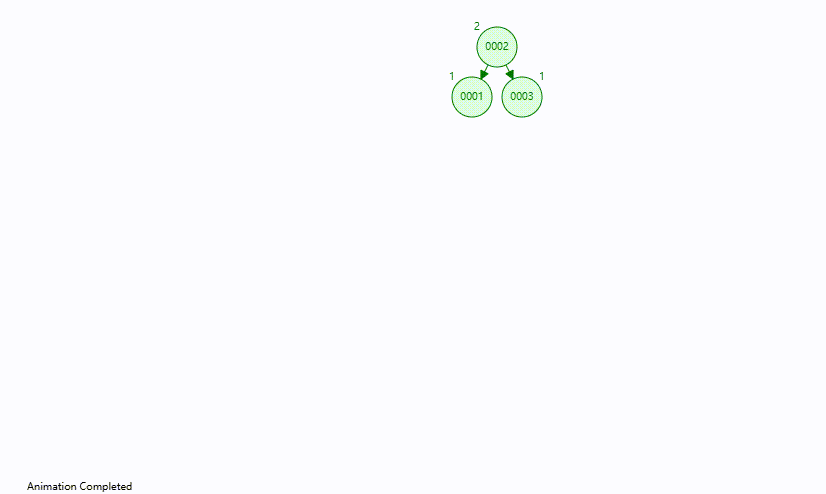
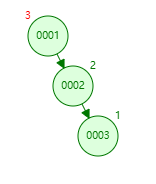
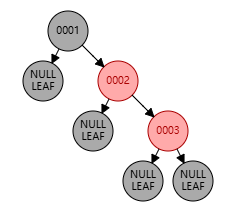
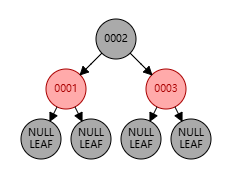
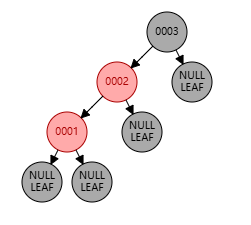
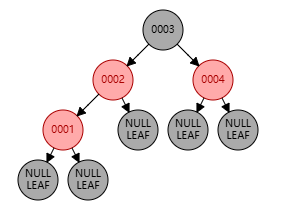
右旋 将节点 0003,0002,0001 依次插入平衡二叉树中
此时节点 0003 的平衡因子为 2,说明其左子树存在失衡
为保持平衡,需要将节点 0003 和 0002 进行 右旋
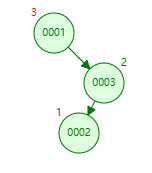
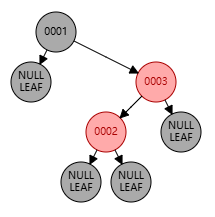
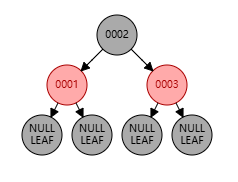
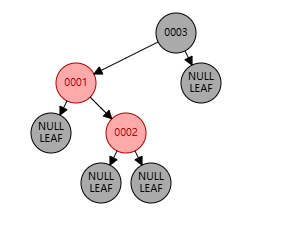
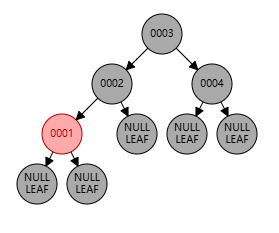
左旋 将节点 0001,0002,0003 依次插入平衡二叉树中
此时节点 0001 的平衡因子为 -2,说明其右子树存在失衡
为保持平衡,需要将节点 0001 和 0002 进行 左旋
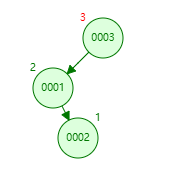
右旋+左旋 将节点 0001,0003,0002 依次插入平衡二叉树中
此时节点 0001 的平衡因子为 -2,说明其右子树存在失衡
但 0002 < 0001 所以需要先将 0003 和 0002 进行右旋,然后再将 0001 和 0002 进行左旋
左旋 + 右旋 将节点 0003,0001,0002 依次插入平衡二叉树中
此时节点 0003 的平衡因子为 2,说明其左子树存在失衡
但 0002 > 0001 所以需要先将 0001 和 0002 进行左旋,然后再将 0003 和 0002 进行右旋
旋转的理解
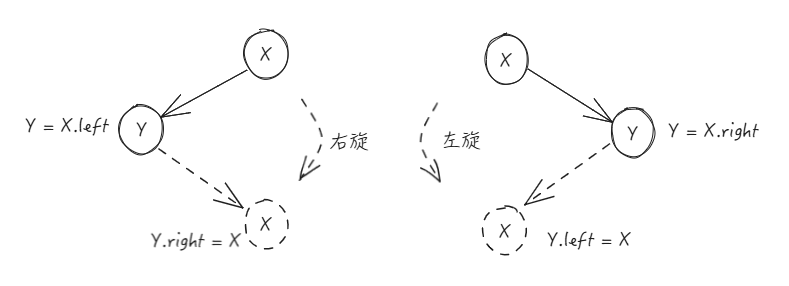
旋转是发生在两个节点间的操作
右旋:将当前节点放到其左子节点的右子节点上
左旋:将当前节点放到其右子节点的左子节点上
旋转的选择:子节点 < 当前节点 => 右旋;当前节点 > 子节点 => 左旋
实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 public class AVLTree <T extends Comparable <T>> { private Node<T> root; public AVLTree () { root = null ; } public void put (T data) { root = insert(root, data); } private Node<T> insert (Node<T> node, T data) { if (node == null ) { return new Node <>(data); } if (data.compareTo(node.data) < 0 ) { node.left = insert(node.left, data); } else if (data.compareTo(node.data) > 0 ) { node.right = insert(node.right, data); } else { return node; } node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right)); int balance = getBalance(node); if (balance > 1 && data.compareTo(node.left.data) < 0 ) { return rightRotate(node); } if (balance < -1 && data.compareTo(node.right.data) > 0 ) { return leftRotate(node); } if (balance > 1 && data.compareTo(node.left.data) > 0 ) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); } if (balance < -1 && data.compareTo(node.right.data) < 0 ) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } return node; } private Node<T> rightRotate (Node<T> node) { Node<T> l = node.left; Node<T> lr = l.right; l.right = node; node.left = lr; node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right)); l.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(l.left), getHeight(l.right)); return l; } private Node<T> leftRotate (Node<T> node) { Node<T> r = node.right; Node<T> rl = r.left; r.left = node; node.right = rl; node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right)); r.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(r.left), getHeight(r.right)); return r; } private int getHeight (Node<T> node) { if (node == null ) { return 0 ; } return node.height; } private int getBalance (Node<T> node) { if (node == null ) { return 0 ; } return getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right); } public void print () { printBFS(root); } private void printBFS (Node<T> node) { if (node == null ) { return ; } Queue<Node<T>> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int level = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < level; i++) { Node<T> tNode = queue.poll(); if (tNode != null ) { System.out.print(tNode.data + " " ); } else { System.out.print("N " ); continue ; } queue.add(tNode.left); queue.add(tNode.right); } System.out.println(); } } private void printDFS (Node<T> node) { if (node == null ) { return ; } List<List<Node<T>>> result = new ArrayList <>(); dfs(node, 0 , result); } private void dfs (Node<T> node, int level, List<List<Node<T>>> result) { if (level == result.size()) { if (node != null ) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(List.of(node))); } else { return ; } } else { if (node != null ) { result.get(level).add(node); } else { result.get(level).add(null ); return ; } } dfs(node.left, level + 1 , result); dfs(node.right, level + 1 , result); } public void delete (T data) { root = delete(root, data); } private Node<T> delete (Node<T> node, T data) { if (node == null ) { return null ; } if (data.compareTo(node.data) < 0 ) { node.left = delete(node.left, data); } else if (data.compareTo(node.data) > 0 ) { node.right = delete(node.right, data); } else { if (node.left == null || node.right == null ) { node = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right; } else { Node<T> temp = minValueNode(node.right); node.data = temp.data; node.right = delete(node.right, temp.data); } } if (node == null ) { return node; } node.height = 1 + Math.max(getHeight(node.left), getHeight(node.right)); int balance = getBalance(node); if (balance > 1 && getBalance(node.left) >= 0 ) { return rightRotate(node); } if (balance > 1 && getBalance(node.left) < 0 ) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); } if (balance < -1 && getBalance(node.right) <= 0 ) { return leftRotate(node); } if (balance < -1 && getBalance(node.right) > 0 ) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } return node; } private Node<T> minValueNode (Node<T> node) { if (node == null ) { return null ; } if (node.left == null ) { return node; } return minValueNode(node.left); } public static void main (String[] args) { AVLTree<Integer> avlTree = new AVLTree <>(); avlTree.put(5 ); avlTree.print(); avlTree.put(3 ); avlTree.print(); avlTree.put(4 ); avlTree.print(); } static class Node <T> { T data; Node<T> left; Node<T> right; int height; public Node (T data) { this .data = data; this .height = 1 ; } } }
红黑树 平衡二叉树为保证树的平衡,在插入和删除的时候可能会触发 logN 次旋转,随着 N 的不断增大,旋转的次数会不断增多。那么有没有一种能减少旋转次数的结构呢?答案就是——红黑树
约束 红黑树对每个节点增加了一个节点颜色的属性
旋转 红黑树的特点就是减少了旋转的次数,通过父节点与祖父节点的位置,以及父节点与叔节点的颜色来判断是否需要旋转
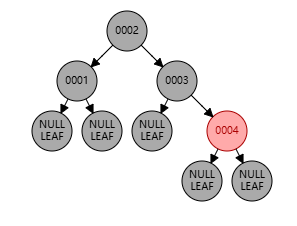
父节点位于祖父节点的右边,且父节点是红色,叔节点是黑色,新增节点为右子节点
上图中:祖父节点为 0001,父节点为 0002,叔节点为 NULL,新增节点为 0003
这种情况下,只需将 0001 左旋 至 0002 的左子节点,并将 父节点置黑,祖父节点置红
父节点位于祖父节点的右边,且父节点是红色,叔节点是黑色,新增节点为左子节点
上图中:祖父节点为 0001,父节点为 0003,叔节点为 NULL,新增节点为 0002
这种情况下,需要先将 0003 右旋 到 0002 的右子节点,然后将 0001 左旋 到 0002 的左子节点,最后将 新增节点置黑,祖父节点置红
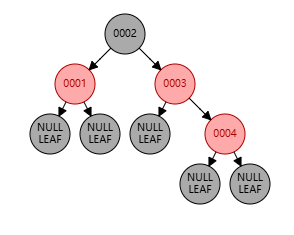
父节点位于祖父节点的右边,且父节点和叔节点都是红色
上图中:祖父节点为 0002,父节点为 0003,叔节点为 0001,新增节点为 0004
这种情况下,无论新增节点是在左子树上还是右子树上,都 不需要旋转调整结构,只需要改变颜色 ,将父节点与叔节点置为黑色,祖父节点置为红色,此处祖父节点为根节点,所以还需重置为黑色
父节点位于祖父节点的左边,且父节点是红色,叔节点是黑色,新增节点为左子节点
上图中:祖父节点为 0003,父节点为 0002,叔节点为 NULL,新增节点为 0001
这种情况下,只需将 0003 右旋 至 0002 的右子节点,并将 父节点置黑,祖父节点置红
父节点位于祖父节点的左边,且父节点是红色,叔节点是黑色,新增节点为右子节点
上图中:祖父节点为 0003,父节点为 0001,叔节点为 NULL,新增节点为 0002
这种情况下,需要先将 0001 左旋 到 0002 的左子节点,然后将 0003 右旋 到 0002 的右子节点,最后将 新增节点置黑,祖父节点置红
父节点位于祖父节点的左边,且父节点和叔节点都是红色
上图中:祖父节点为 0003,父节点为 0002,叔节点为 0004,新增节点为 0001
与父节点位于祖父节点的右边,且父节点和叔节点都是红色的情况一致,都 不需要旋转调整结构,只需要改变颜色
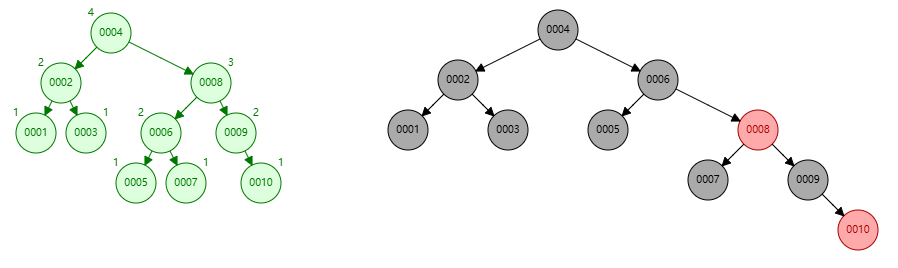
对比 AVL-Trees 将 0001~0010 分别插入平衡二叉树与红黑树中
红黑树舍弃了平衡二叉树严格要求的左右子树高度差,取而代之的是节点颜色
从而牺牲部分的查找性能来换取插入和删除的性能
实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 public class RBTee <T extends Comparable <T>> { private static final boolean RED = true ; private static final boolean BLACK = false ; private Node<T> root; public RBTee () { this .root = null ; } public void put (T value) { Node<T> newNode = new Node <>(value); insert(newNode); } private void insert (Node<T> newNode) { Node<T> current = root; Node<T> parent = null ; while (current != null ) { parent = current; if (newNode.data.compareTo(current.data) < 0 ) { current = current.left; } else { current = current.right; } } newNode.parent = parent; if (parent == null ) { root = newNode; } else if (newNode.data.compareTo(parent.data) < 0 ) { parent.left = newNode; } else { parent.right = newNode; } fixAfterInsertion(newNode); } private void fixAfterInsertion (Node<T> newNode) { while (newNode != root && newNode.parent.color == RED) { Node<T> parent = newNode.parent; Node<T> grandParent = parent.parent; if (parent == grandParent.left) { Node<T> uncle = grandParent.right; if (uncle != null && uncle.color == RED) { parent.color = BLACK; uncle.color = BLACK; grandParent.color = RED; newNode = grandParent; } else { if (newNode == parent.right) { leftRotate(parent); newNode = parent; parent = newNode.parent; } rightRotate(grandParent); parent.color = BLACK; grandParent.color = RED; newNode = parent; } } else { Node<T> uncle = grandParent.left; if (uncle != null && uncle.color == RED) { parent.color = BLACK; uncle.color = BLACK; grandParent.color = RED; newNode = grandParent; } else { if (newNode == parent.left) { rightRotate(parent); newNode = parent; parent = newNode.parent; } leftRotate(grandParent); parent.color = BLACK; grandParent.color = RED; newNode = parent; } } } root.color = BLACK; } private void leftRotate (Node<T> node) { Node<T> rightSon = node.right; Node<T> leftGrandson = rightSon.left; rightSon.left = node; node.right = leftGrandson; if (leftGrandson != null ) { rightSon.left.parent = node; } rightSon.parent = node.parent; if (node.parent == null ) { root = rightSon; } else if (node == node.parent.left) { node.parent.left = rightSon; } else { node.parent.right = rightSon; } node.parent = rightSon; } private void rightRotate (Node<T> node) { Node<T> leftSon = node.left; Node<T> rightGrandson = leftSon.right; leftSon.right = node; node.left = rightGrandson; if (rightGrandson != null ) { leftSon.right.parent = node; } leftSon.parent = node.parent; if (node.parent == null ) { root = leftSon; } else if (node == node.parent.right) { node.parent.right = leftSon; } else { node.parent.left = leftSon; } node.parent = leftSon; } public void delete (T value) { Node<T> node = find(value); if (node == null ) { return ; } delete(node); } private void delete (Node<T> node) { Node<T> son, parent; boolean color; if (node.left != null && node.right != null ) { node = minValueNode(node.right); } if (node.left != null ) { son = node.left; } else { son = node.right; } parent = node.parent; color = node.color; if (son != null ) { son.parent = parent; } if (parent == null ) { root = son; } else if (node == parent.left) { parent.left = son; } else { parent.right = son; } if (color == BLACK) { fixAfterDeletion(son, parent); } } private void fixAfterDeletion (Node<T> node, Node<T> parent) { Node<T> temp; while (node != root && (node == null || node.color == BLACK)) { if (parent.left == node) { temp = parent.right; if (temp.color == RED) { temp.color = BLACK; parent.color = RED; leftRotate(parent); temp = parent.right; } if ((temp.left == null || temp.left.color == BLACK) && (temp.right == null || temp.right.color == BLACK)) { temp.color = RED; node = parent; parent = node.parent; } else { if (temp.right == null || temp.right.color == BLACK) { temp.left.color = BLACK; temp.color = RED; rightRotate(temp); temp = parent.right; } temp.color = parent.color; parent.color = BLACK; temp.right.color = BLACK; leftRotate(parent); node = root; } } else { temp = parent.left; } } } private Node<T> minValueNode (Node<T> node) { if (node.left == null ) { return node; } return minValueNode(node.left); } private Node<T> find (T data) { Node<T> current = root; while (current != null ) { if (data.compareTo(current.data) == 0 ) { return current; } else if (data.compareTo(current.data) < 0 ) { current = current.left; } else { current = current.right; } } return null ; } static class Node <T> { T data; boolean color; Node<T> left; Node<T> right; Node<T> parent; public Node (T data) { this .data = data; this .color = RED; this .left = null ; this .right = null ; this .parent = null ; } } }
TreeMap 与 HashMap 和 LinkedHashMap 相似的是,他们内部都会有一个实现了 Map.Entry 的 Entry,这个 Entry 是他们存储的基本单元
TreeMap 的特点是它底层基于红黑树来实现,所以可以做到 Entry 的有序性
put 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public V put (K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null ) { compare(key, key); root = new Entry <>(key, value, null ); size = 1 ; modCount++; return null ; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null ) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0 ) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0 ) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null ); } else { if (key == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0 ) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0 ) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null ); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry <>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0 ) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 private void fixAfterInsertion (Entry<K,V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateLeft(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } else { Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } } root.color = BLACK; } private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf (Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null ? null : p.parent); } private static <K,V> boolean colorOf (Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color); }
remove 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public V remove (Object key) { Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); if (p == null ) return null ; V oldValue = p.value; deleteEntry(p); return oldValue; } private void deleteEntry (Entry<K,V> p) { modCount++; size--; if (p.left != null && p.right != null ) { Entry<K,V> s = successor(p); p.key = s.key; p.value = s.value; p = s; } Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right); if (replacement != null ) { replacement.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null ) root = replacement; else if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = replacement; else p.parent.right = replacement; p.left = p.right = p.parent = null ; if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == null ) { root = null ; } else { if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); if (p.parent != null ) { if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = null ; else if (p == p.parent.right) p.parent.right = null ; p.parent = null ; } } }
未完待续…